[Java] 컬렉션 프레임웍(Collection Framework)
in Java on Java Collection
컬렉션 프레임웍(Collection Framework)이란? 다수의 데이터를 다루고 표현하기 위한 단일화 된 구조이다.
1. 컬렉션 프레임웍(Collection Framework)
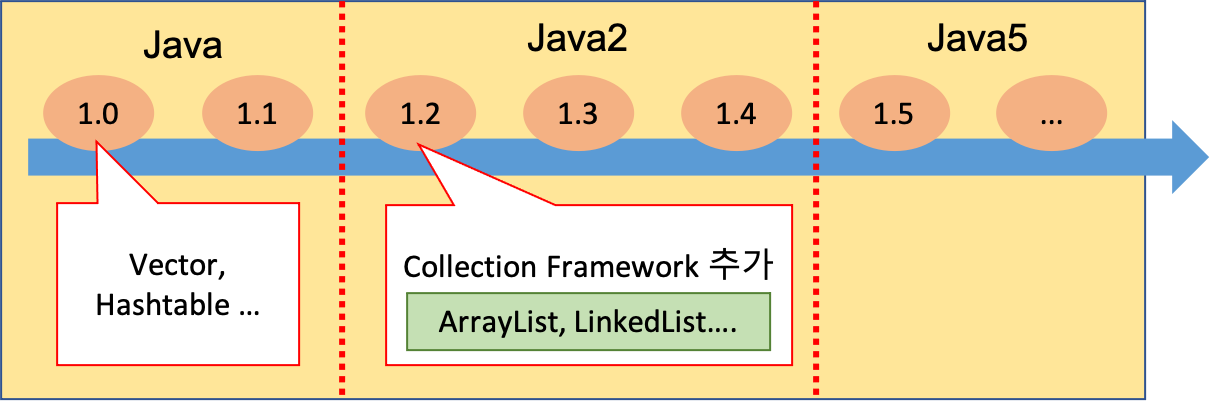
JDK1.2 이전까지는 Vector, Hashtable, Properties와 같은 컬렉션 클래스를 사용하다 JDK1.2 이후 부터 컬렉션 프레임웍이 등장하면서 다양한 종류의 컬렉션 클래스가 추가되었다.
자바에서 자료구조를 바탕으로 객체나 데이터들을 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 만들어 놓은 자료구조 라이브러리(Java API)들을 컬렉션 프레임워크라고한다. 대표적으로는 List, Set, Map, Stack, Queue 등이 있다.
1.2. 컬렉션 프레임웍의 핵심 인터페이스 - List, Set, Map
컬렉션 프레임웍의 대표적인 List, Set, Map 에서 인터페이스 List와 Set은 공통적인 부분을 다시 Collection 인터페이스로 정의되며, Map은 다른 형태로 데이터를 다루기 때문에 상속계층도가 아래와 같다.
| 인터페이스 | 특징 | 구현클래스 |
|---|---|---|
List<E> | 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합. 데이터의 중복 허용 | ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector 등 |
Set<E> | 순서를 유지하지 않는 데이터의 집합. 데이터의 중복 허용 x | HashSet, TreeSet 등 |
Map<K, V> | 키(Key)와 값(Value)의 쌍(Pair)으로 이루어진 데이터의 집합 순서는 유지 안됨, 키 중복 안됨 | HashMap, TreeMap, HashTable 등 |
Vector, Hashtable 등 클래스들은 Java 1.0 부터 만들어져 컬렉션 프레임워크가 생기기전부터 있던 것들이다.
Vector와 List객체의 차이는 동기화(Synchronization) 기능 여부이다. 멀티쓰레드 프로그래밍에서 일관성을 유지하기 위해서 Vector는 List가 나오기전까지 사용되었으며, Java2(1.2)부터 Collection 구현객체인 List가 나오면서 Vector는 거의 사용되지 않으며 Collection 인터페이스인 List, Set, Map 등을 사용한다.
1.3. Collection 인터페이스
Collection 인터페이스 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(Object o) boolean addAll(Collection c) | 지정된 객체(o) 또는 Collection(c)의 객체들을 Collection에 추가한다. |
| void clear() | Collection의 모든 객체를 삭제한다. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 지정된 객체(o) 또는 Collection의 객체들이 Collection에 포함되어 있는 확인한다. |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 동일한 Collection 인지 비교한다. |
| int hashCode() | Collection의 hash code를 반환한다. |
| boolean isEmpty() | Collection이 비어있는지 확인한다. |
Iterator iterator() | Collection의 Iterator을 얻어서 반환한다. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 지정된 객체를 삭제한다. |
| boolean removeAll(Collection c) | 지정된 Collection에 포함된 객체들을 삭제한다. |
| boolean retainAll(Collection c) | 지정된 Collection에 포함된 객체만을 남기고 다른 객체들은 Collection에서 삭제하며, true/false를 반환한다. |
| int size() | Collection에 저장된 객체의 개수를 반환한다. |
| Object[] toArray() | Collection에 저장된 객체를 객체배열(Object[])로 반환한다. |
| Object[] toArray(Object[] a) | 지정된 배열에 Collection의 객체를 저장해서 반환한다. |
2. List 인터페이스
List 인터페이스는 중복을 허용하면서 저장순서가 유지되는 컬렉션을 구현하는데 사용된다.
구현클래스로는 ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, Stack 등이 있다.
2-1. List 구조
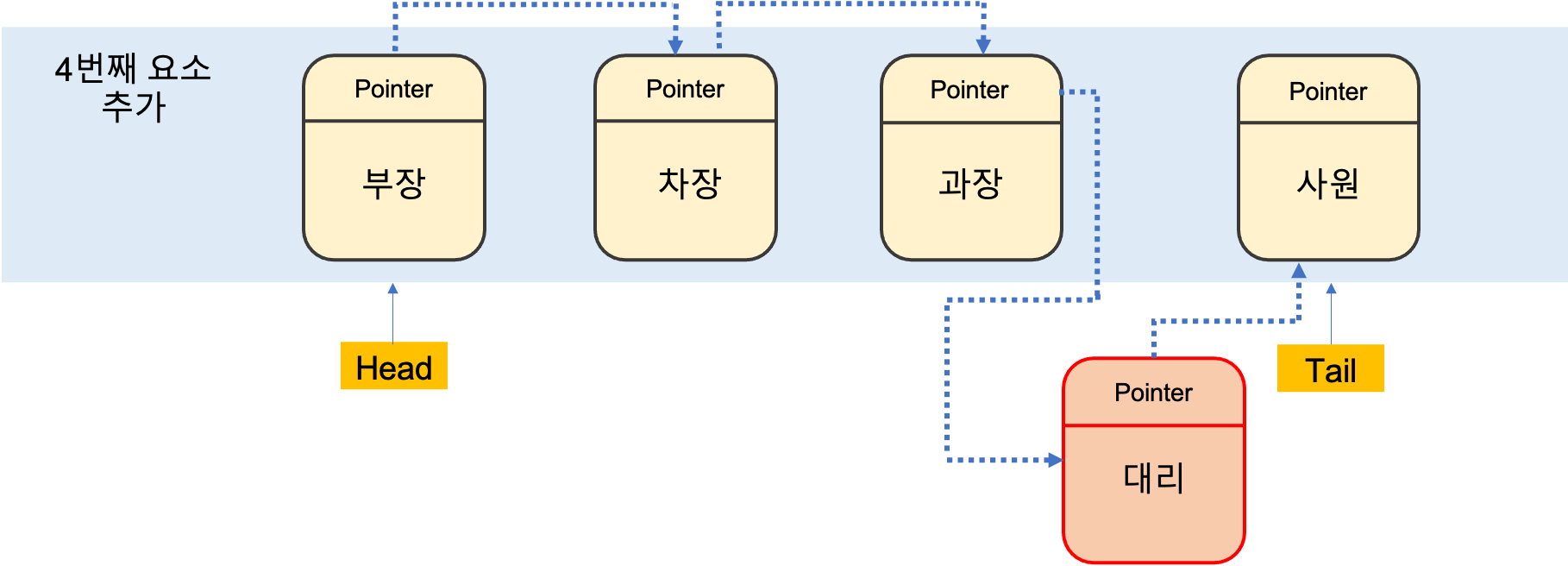
리스트는 배열이 가지고 있는 인덱스라는 장점을 버리고 대신 빈틈없이 데이터를 적재되는 형태로 순서대로 한 줄로 저장되는 자료구조이며, 데이터가 서로 연결 된 선형구조 형태이다. List는 Array 와 다르게 물리적으로 연속된 위치가 아닌 떨어진 영역에 저장된다는 점이다.
리스트에서는 인덱스가 중요하지 않으며 리스트 데이터 구조의 핵심은 요소(데이터)들 간의 순서이다. 즉 순서가 있는 데이터의 리스트입니다.
위와 같이 대리라는 요소가 추가 될때 List 의 자료 구조는 포인터(pointer)가 다음 요소의 메모리의 위치를 가르키는 개념이다.
자바 언어에서는 다른 언어와 다르게 Array(배열)과 List(리스트)를 각각 따로 지원해주고 있다는거에 대해서도 생각해볼 필요가 있다.
2-2. List 예제
List 인터페이스를 ArrayList 클래스로 구현한 예제이다.
package collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("부장");
list.add("차장");
list.add("대리");
list.add("과장");
list.add("사원");
System.out.println("----- before -----");
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
//System.out.println("> before =" + list.toString());
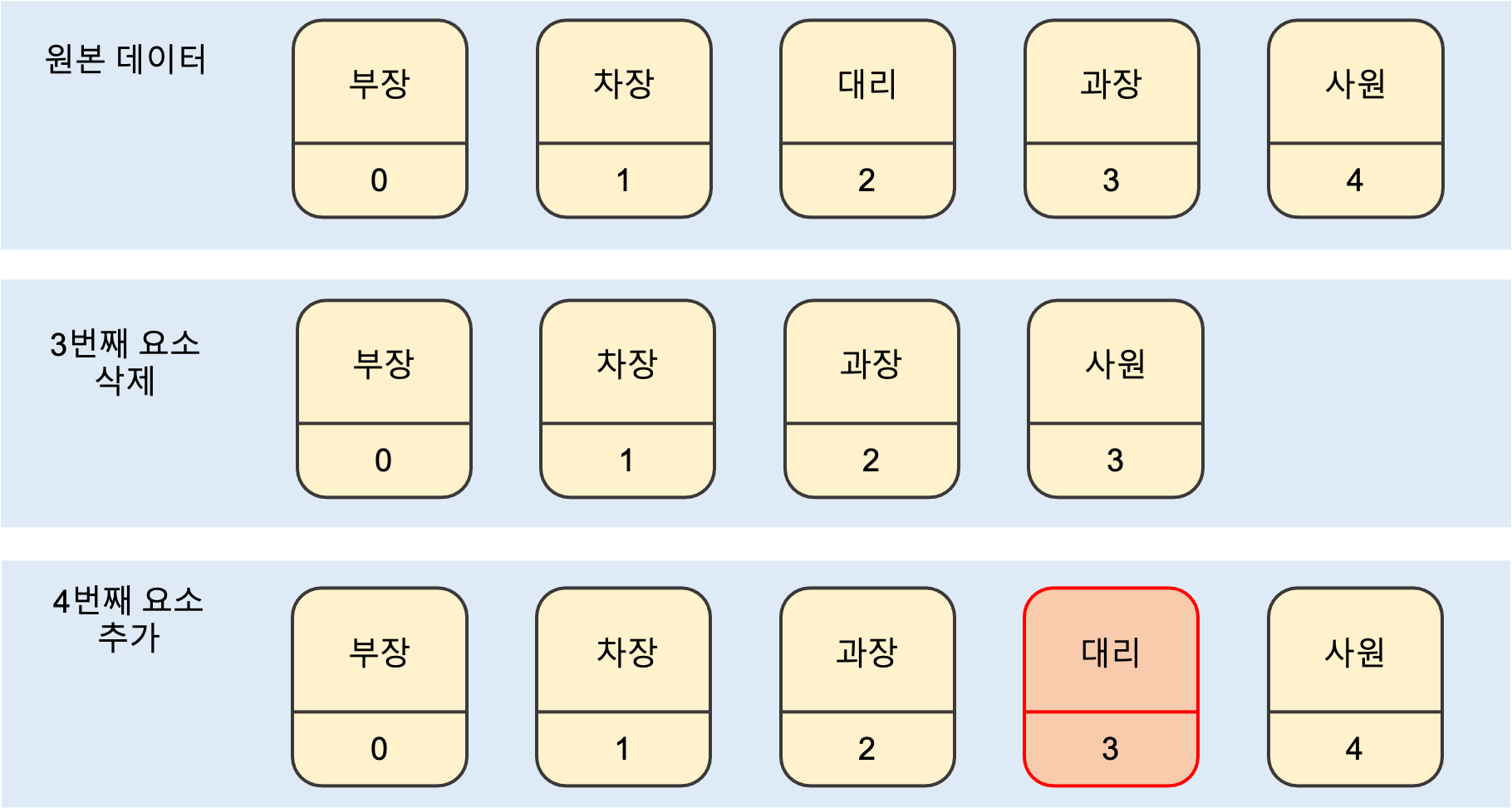
//요소 삭제 및 추가
list.remove(2);
list.add(3, "대리");
System.out.println("----- after -----");
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
//System.out.println("> after =" + list.toString());
}
}
console
----- before -----
부장
차장
대리
과장
사원
----- after -----
부장
차장
과장
대리
사원
2-3. List 인터페이스의 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| void add(int index, Object element) | 지정된 위치(index)에 객체(element) 또는 컬렉션에 포함된 객체들을 추가한다. |
| Object get(int index) | 지정된 위치(index)에 있는 객체를 반환한다. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 지정된 객체의 위치(index)를 반환한다.(순방향 검색) |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 지정된 객체의 위치(index)륿 반환한다.(역방향 검색) |
| ListIterator listIterator() ListIterator listIterator(int index) | List의 객체에 접근 할 수 있는 ListIterator 반환한다. |
| Object remove(int index) | 지정된 위치(index)에 있는 객체를 삭제하고 삭제된 객체를 반환한다. |
| Object set(int index, Object element) | 지정된 위치(index)에 객체(element)를 저장한다. |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 지정된 범위(fromIndex 부터 toIndex)에 있는 객체를 반환한다. |
3. Set 인터페이스
Set 이란? 집합이라는 뜻이다. Set 인터페이스는 중복을 허용하지 않고 저장순서가 유지되지 않은 컬렉션 클래스를 구현하는데 사용되며 빠른 Lookup(데이터가 있는지 탐색)이 필요할때 주로 쓰인다. Set 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스로는 HashSet, TreeSet 등이 있다.
Set에서 요소들이 저장될 때 저장할 요소의 값의 hash 값을 구해서 해쉬값에 해당하는 공간(bucket)에 값을 저장하기 때문에 순서가 없다. 해쉬 기반이기에 빠른 접근이 가능하다.
3-1. Set 구조
같은 요소(데이터)를 중복을 원치 않을 경우에 사용한다. 즉 중복된 값을 제거하고 순서가 상관없을 때 사용된다.
3-2-1. Set 예제
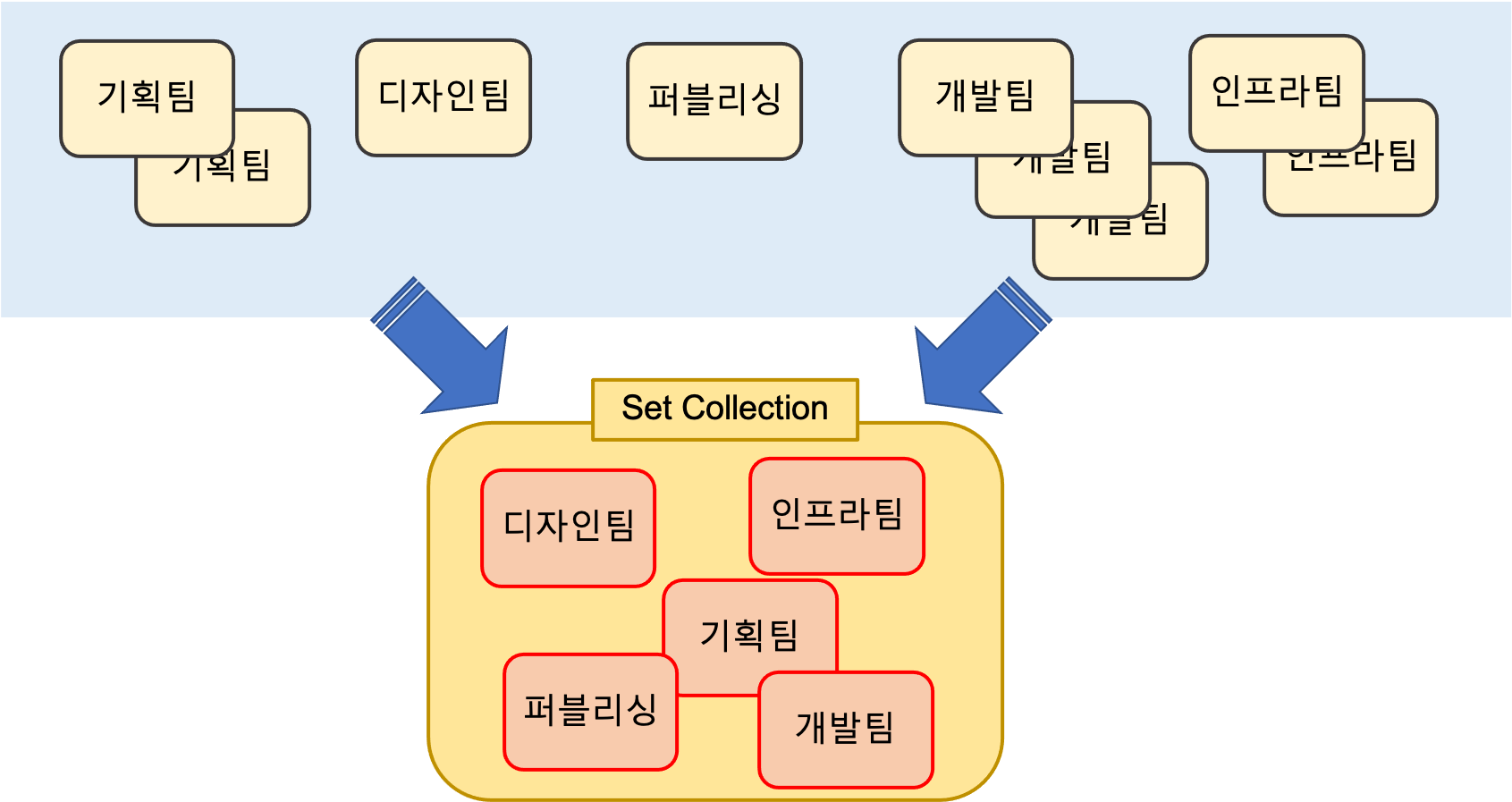
Set 인터페이스를 HashSet 클래스로 구현한 예제이다. 같은 요소(데이터)를 중복을 원치 않을 경우에 사용한다.
package collection.list;
import java.util.*;
public class SetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> deptList = new ArrayList<String>();
deptList.add("기획팀");
deptList.add("기획팀");
deptList.add("디자인팀");
deptList.add("퍼블리싱");
deptList.add("개발팀");
deptList.add("개발팀");
deptList.add("개발팀");
deptList.add("인프라팀");
deptList.add("인프라팀");
System.out.println("----- <List> -----");
Iterator it = deptList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
Set<String> deptSet = new HashSet<String>();
deptSet.add("기획팀");
deptSet.add("기획팀");
deptSet.add("디자인팀");
deptSet.add("퍼블리싱");
deptSet.add("개발팀");
deptSet.add("개발팀");
deptSet.add("개발팀");
deptSet.add("인프라팀");
deptSet.add("인프라팀");
System.out.println("----- <Set> -----");
Iterator hi = deptSet.iterator();
while(hi.hasNext()){
System.out.println(hi.next());
}
}
}
console
----- <List> -----
기획팀
기획팀
디자인팀
퍼블리싱
개발팀
개발팀
개발팀
인프라팀
인프라팀
----- <Set> -----
디자인팀
인프라팀
기획팀
개발팀
퍼블리싱
3-2-2. Set 집합 예제
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> A = new HashSet<Integer>();
A.add(1);
A.add(2);
A.add(3);
Set<Integer> B = new HashSet<Integer>();
B.add(3);
B.add(4);
B.add(5);
Set<Integer> C = new HashSet<Integer>();
C.add(1);
C.add(2);
System.out.println(A.containsAll(B)); // false
System.out.println(A.containsAll(C)); // true
//A.addAll(B);
//A.retainAll(B);
//A.removeAll(B);
Iterator hi = A.iterator();
while(hi.hasNext()){
System.out.println(hi.next());
}
}
- 참고 URL: https://opentutorials.org/course/1223/6446
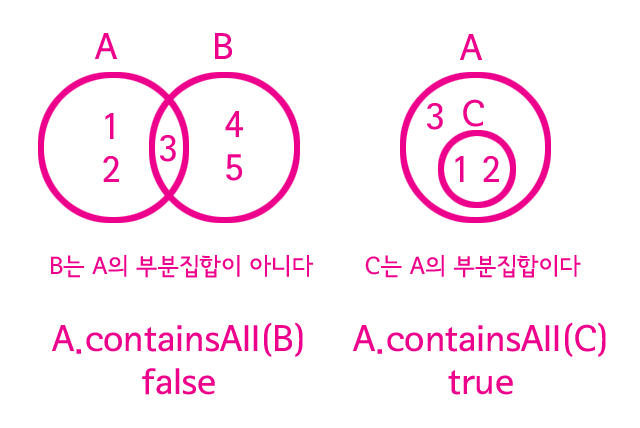
부분집합 (subset)
System.out.println(A.containsAll(B)); // false
System.out.println(A.containsAll(C)); // true
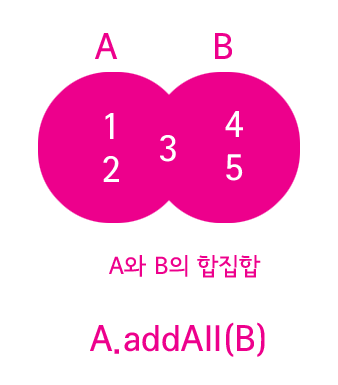
합집합(union)
A.addAll(B);
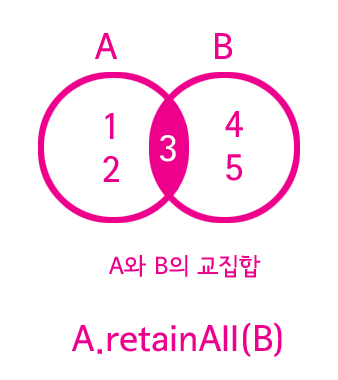
교집합(intersect)
A.retainAll(B);
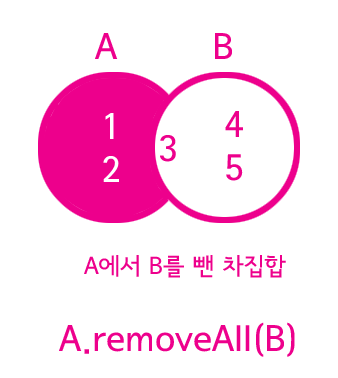
차집합(difference)
A.removeAll(B);
- 이미지 출처: https://opentutorials.org/course/1223/6446
3-3. Set 인터페이스의 메서드
Set 인터페이스에는 따로 메서드가 없으며, Collection 인터페이스 API와 동일하다. Set컬렉션의 경우에는 저장 순서가 유지되지 않는다. 인덱스 개념이 없기 때문에 List 인터페이스처럼 따로 정의되어 있는 get(int Index) 메서드 등 API가 없기 때문에 Collection 인터페이스에 정의되어 있는 Iterator를 통해서 데이터에 접근해서 가져온다.
- Iterator iterator() : Collection의 Iterator을 얻어서 반환한다.
3. Map 인터페이스
Map 인터페이스는 키(Key)와 값(Value)을 하나의 쌍인 데이터 구조를 가진 컬렉션 클래스 구현하는데 사용된다.
요소의 저장 순서를 유지하지 않습니다. 키는 중복을 허용하지 않지만, 값의 중복은 허용하며 대표적인 Map 컬렉션 클래스에 속하는 클래스는 다음과 같습니다. HashMap, Hashtable, LinkedHashMap, TreeMap 등이 있다.
3-1. Map의 구조
예를 굳이 들자면 한 회사에 사번<key>은 고유하지만 이름<value>은 동명이인 있을 수 있다. 또한 사번은 고유하기 때문에 이름을 가져올 수 있다.
3-2. Map 예제
HashMap 클래스는 Map 컬렉션 클래스를 구현하는 클래스 중 하나이다. JDK 1.2부터 제공된 HashMap 클래스는 해시 알고리즘을 사용하여 검색 속도가 빠르다.
Map 자체에는 Iterator가 없기에 Map의 entrySet() 이용해 Map.Entry의 데이터 타입으로 변경해서 전체 데이터를 반복해서 데이터를 접근한다.
package collection.list;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Object> employee = new HashMap<String, Object>();
employee.put("EMP121", "김준영");
employee.put("EMP122", "김욱");
employee.put("EMP305", "박재현");
employee.put("EMP311", "이유리");
employee.put("EMP314", "정연호");
employee.put("EMP545", "김욱");
System.out.println(employee.get("EMP121"));
System.out.println(employee.get("EMP122"));
System.out.println(employee.get("EMP314"));
System.out.println(employee.get("EMP545"));
iteratorUsingForEach(employee);
//iteratorUsingIterator(employee);
}
static void iteratorUsingForEach(HashMap map){
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
static void iteratorUsingIterator(HashMap map){
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> i = entries.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = i.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" : "+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
console
김준영
김욱
정연호
김욱
EMP305 : 박재현
EMP121 : 김준영
EMP122 : 김욱
EMP311 : 이유리
EMP314 : 정연호
EMP545 : 김욱
3-3. Map 인터페이스의 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| void clear() | Map의 모든 객체를 삭제한다. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 지정된 key객체와 일치하는 Map의 Key객체가 있는지 확인한다. |
| boolean containsValue(Object Value) | 지정된 value객체와 일치하는 Map의 value객체가 있는지 확인한다. |
| Set entrySet() | Map에 저장되어 있는 key-value쌍을 Map.Entry타입의 객체로 저장한 Set으로 반환한다. |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 동일한 Map인지 비교한다. |
| Object get(Object key) | 지정한 key객체에 대응하는 value객체를 찾아서 반환한다. |
| int hashCode() | 해시코드를 반환한다. |
| boolean isEmpty() | Map이 비어있는지 확인한다. |
| Set keySet() | Map에 저장된 모든 key객체를 반환한다. |
| Object put(Object key, Object value) | Map에 value객체를 key객체에 연결(mapping)하여 저장한다. |
| void putAll(Map t) | 지정된 Map의 모든 key-value 쌍을 추가한다. |
| Object remove(Object key) | 지정한 key객체와 일치하는 key-value객체를 삭제한다. |
| int size() | Map에 저장된 key-value쌍의 개수를 반환한다. |
| Collection values() | Map에 저장된 모든 value객체를 반환한다. |
[참고]
- https://seeit.kr/36
- http://tcpschool.com/java/java_collectionFramework_list
- https://opentutorials.org/module/1335/8636
- https://opentutorials.org/course/1223/6446